In an era of chatgpt-enabled applications, most of us would have come across a term called as foundation model. In this article we will go through the basics of foundation model with respect to Large Language Models
In this article we will go through these topics in simple language:
- What are Foundation Models?
- What are Large Language Models?
- Fundamental Architecture inside LLM?
- Types of LLMs.
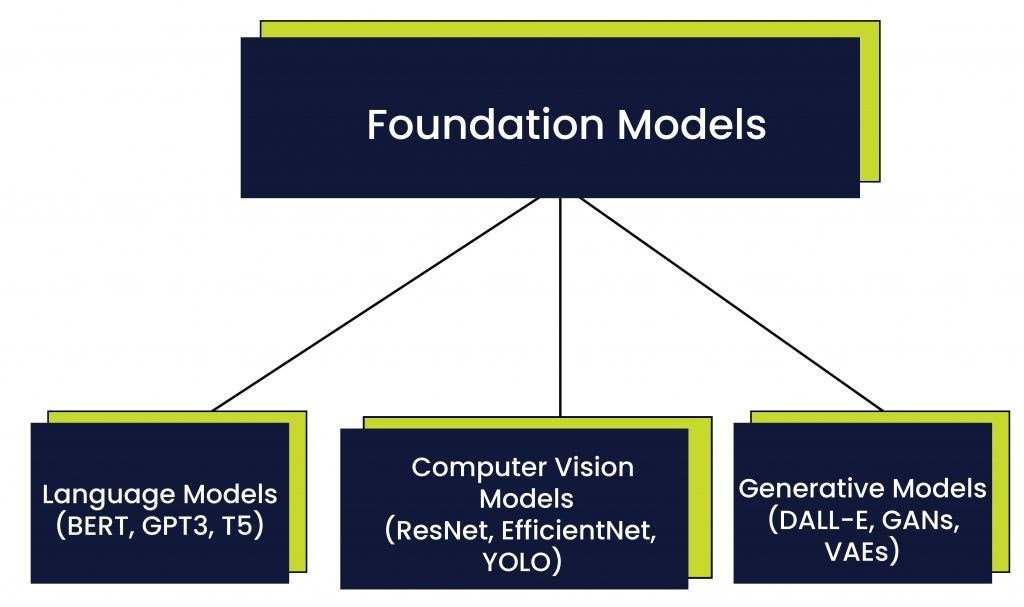
What are Foundation Models?
If you go to any Indian restaurant and order Chicken Tikka Masala, it arrives at your table in no time. But if you were to make the same dish from scratch, it would take much longer. Most people assume that restaurants prepare curries in advance and simply reheat them when an order comes in. However, that would be a waste of resources if there aren’t any orders for that particular dish.
Instead, restaurants use a common base gravy for a wide range of curries—such as Onion-Tomato Gravy or Onion-Spinach-Ginger Gravy. When an order hits the kitchen, chefs take this foundation gravy, add the required proteins, herbs, and veggies, and create a distinct curry as per the order. This approach saves time, ensures consistency, and allows for quick adaptation to different recipes.
Now, we can apply this analogy to our AI models.
Foundation Models are like these base gravies. They are trained on vast amounts of data and serve as a starting point for a range of applications. Unlike a base gravy, where we choose common ingredients, foundation models are built by training on diverse and extensive datasets.
For example, in Natural Language Processing (NLP), which deals with human language and conversation, a foundation model is trained on massive amounts of text data available on the internet (while ensuring ethical considerations). The resulting model acts as a foundation for various NLP tasks, such as chatbots, translations, and text generation.
Just like chefs fine-tune a base gravy to create different dishes, developers fine-tune foundation models to adapt them for specific use cases.
What are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models is one such foundation model that is trained on vast textual data using Deep Learning to understand and generate human type of language.
Much like our foundation gravy, LLMs act as a foundation for language-based applications. Instead of training a model from scratch for every NLP task, we build on this pre-trained foundation model and fine-tune them for specific purposes.
Fundamental Architecture inside LLM?
At the heart of LLMs lies the Transformer architecture, introduced in the groundbreaking paper "Attention is All You Need" by Vaswani et al. This architecture revolutionized NLP as this model helps to understand context and relationships between words more effectively.
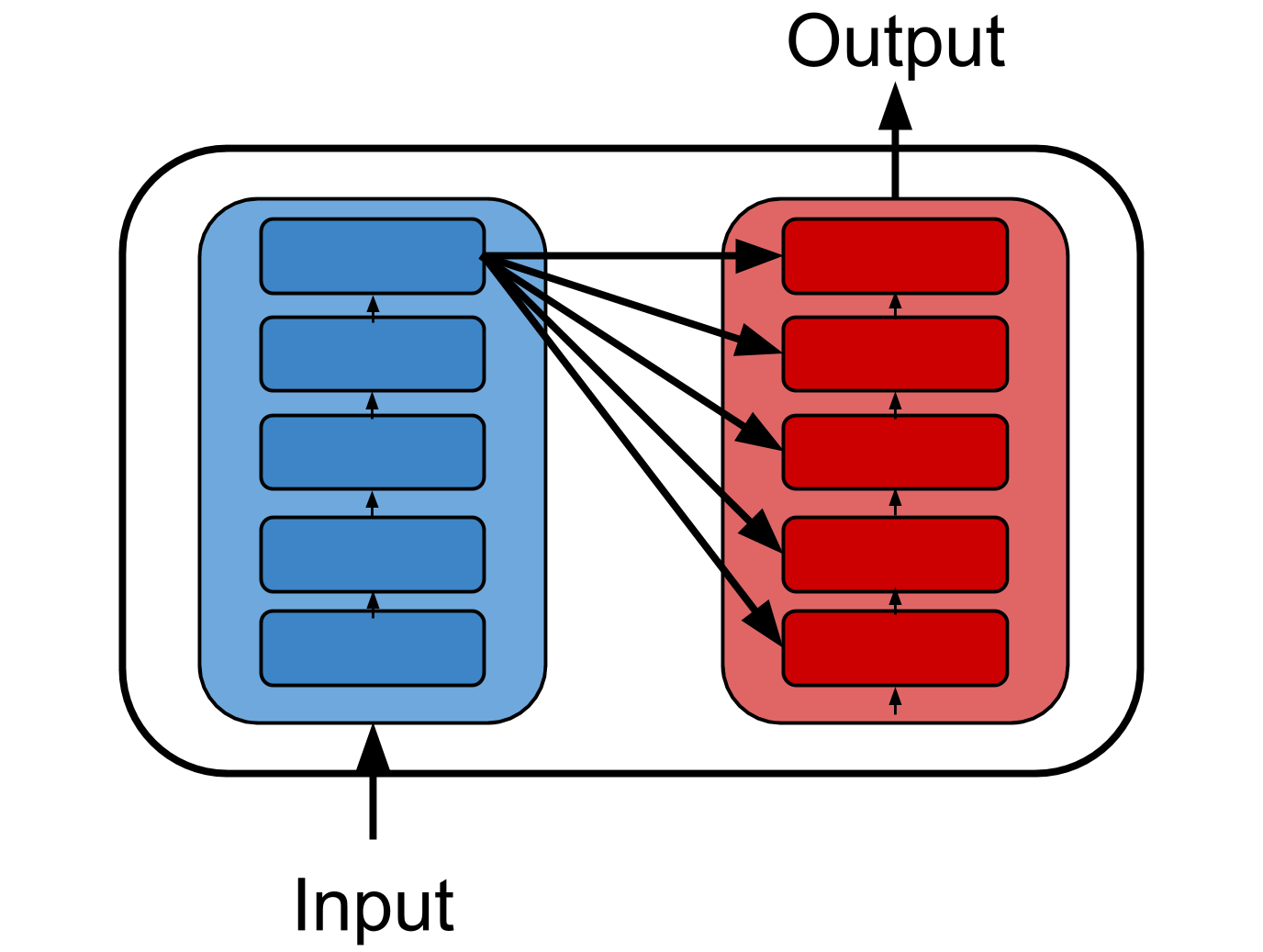
The original paper was developed for a language translation use case. The input is in one language, say English, and the output is in another language, say Hindi. The blue section represents the Encoder, while the red section represents the Decoder.
- The
Encoderis responsible for understanding the input language. - The
Decoderthen generates the output language by interpreting the encoded information.
This encoder-decoder framework laid the foundation for many modern NLP models, enabling efficient translation, text generation, and other complex language tasks.
Types of LLMs?
Since the original encoder-decoder architecture was designed for translation tasks, it is not ideally suited for other tasks like text classification, topic selection, generative tasks, and more.
Encoder Only LLM - Representation Models
To address this, a general-purpose model was introduced in 2018: Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT). This model served as a foundational architecture for Language AI in the years to come.
- The
Encoder-onlyarchitecture focuses on understanding and representing language rather than generating it. - It learns the nuances and contextual
representations of languageeffectively. - Ideal for tasks that require deep language comprehension.
Decoder Only LLM - Generative Models
Similar to the Encoder-only architecture, a Decoder-only architecture was proposed in 2018 for generative tasks. This model is known as Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT).
- The
Decoder-onlyarchitecture is designed to generate text based on a given prompt or input. - It is widely used for conversational AI, creative writing, and content generation.
Thus, these two foundational LLM architectures are broadly used for a variety of applications today.
Use Cases.
Encoder-Only LLMs (BERT and similar models):
- Text classification
- Sentiment analysis
- Information retrieval
- Question answering
Decoder-Only LLMs (GPT and similar models):
- Text generation
- Conversational AI (chatbots, virtual assistants)
- Summarization